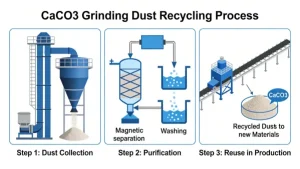
Calcium carbonate (chemical formula: CaCO₃) is a common inorganic compound widely found in natural minerals such as marble, limestone, and calcite. Due to its wide availability, low cost, and excellent physical and chemical properties, it has extremely important application value in industrial production. The following will detail its core composition, main physical properties, and industrial application scenarios.
I. Core Composition
The main component of calcium carbonate is calcium carbonate itself, which is formed by the combination of calcium ions (Ca²⁺) and carbonate ions (CO₃²⁻) through ionic bonds. The purity of its natural mineral raw materials varies, and products with different purity levels can be obtained through industrial processing to meet the application requirements of different fields.
II. Main Physical Properties
Calcium carbonate has stable physical properties, which are specifically manifested as follows:
Appearance and State: At room temperature, it is a white, odorless, and tasteless powder or crystal. Among them, calcite is rhombohedral crystal, aragonite is orthorhombic crystal, and the whole is non-toxic, making it a commonly used non-toxic inorganic material in industry.
Solubility: It is slightly soluble in water and ethanol. The solubility in water at 20℃ is only about 0.0013g/100mL; however, it can react with and dissolve in dilute acids (such as hydrochloric acid and nitric acid), releasing carbon dioxide gas during the dissolution process. This property provides a basis for some of its industrial applications.
Density and Hardness: The density of powdered calcium carbonate is about 2.71g/cm³, with slight differences among different crystal forms. The density of calcite is 2.6-2.8g/cm³, and that of aragonite is about 2.9-3.0g/cm³; the Mohs hardness is low, with calcite having a hardness of 3 and aragonite 3.5-4. which can be slightly scratched with nails or a knife, facilitating processing and grinding.
Melting Point and Thermal Stability: It has no definite melting point under normal pressure and will decompose into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide when heated to about 825℃; the melting point can only be measured as about 1339℃ under high pressure. This thermal decomposition property is widely used in the production processes of the building materials and other fields.
Other Properties: It has a certain hygroscopicity and will absorb a small amount of moisture in a humid environment; it is non-conductive and belongs to an insulator; it is stable to light and not easy to decompose under ultraviolet radiation, with good storage stability.
III. Industrial Application Scenarios
Relying on its excellent properties, calcium carbonate has core applications in multiple industrial fields. Different industries will select different types of products such as light calcium carbonate, heavy calcium carbonate, or nano-calcium carbonate according to their needs. The specific applications are as follows:
1. Plastic Industry: Modified Filler
As one of the most commonly used inorganic fillers in the plastic industry, it can be widely applied to various plastic products such as polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC, and ABS. Its addition can not only significantly reduce the cost of plastic raw materials but also improve the rigidity, heat resistance, and dimensional stability of plastics, while enhancing processing fluidity to facilitate injection molding, extrusion, and other processes. Common application products include PVC pipes, plastic films, plastic toys, and home appliance casings.
2. Rubber Industry: Reinforcement and Filling
It is suitable for the filling and reinforcement of natural rubber and synthetic rubber. It can reduce the amount of rubber raw materials to control costs, and effectively improve the tensile strength, tear strength, wear resistance, and hardness of rubber products. Typical application scenarios include tires (inner tube and outer tube filling), rubber seals, rubber hoses, conveyor belts, shoe soles, and other rubber products with medium performance requirements.
3. Coating and Ink Industry: Extender Pigment/Filler
In the coating field (covering water-based coatings, solvent-based coatings, and powder coatings), as an extender pigment, it can improve the hiding power, adhesion, weather resistance, and scrub resistance of coatings, while reducing gloss to meet the needs of matte coatings and reducing the amount of resin to control production costs; in the ink industry, it can improve the fluidity and printability of inks, enhance the whiteness and hiding power of printed products, and is widely used in offset printing inks, gravure printing inks, and other products.
4. Papermaking Industry: Paper Filler and Coating
It is a core filler in the papermaking industry, divided into acidic papermaking fillers and alkaline papermaking fillers (light calcium carbonate is more suitable for alkaline papermaking processes). Adding it to paper can improve whiteness, opacity, smoothness, and printability, reduce the amount of pulp (lowering wood consumption), and improve paper ink absorption; adding calcium carbonate to the paper surface coating can also enhance paper gloss and surface strength, meeting the production needs of high-grade printing papers such as coated paper.
5. Building Materials Industry: Core Raw Material and Additive
It has extremely wide applications in the building materials field: first, as a core raw material for cement production, limestone (mainly composed of calcium carbonate) is calcined at high temperature to generate calcium oxide, which participates in the hydration reaction of cement; second, as an admixture added to concrete or mortar, it improves construction workability, enhances product strength and durability, and reduces production costs; third, it is used in the production of new building materials such as aerated concrete blocks, gypsum boards, and artificial marble. For example, artificial marble uses calcium carbonate as the main raw material, mixed with resin, and formed through pressing and curing, with both aesthetics and durability.
6. Other Industrial Fields
In addition to the above core fields, calcium carbonate also plays a role in many industries: in the metallurgical industry, it is used as a flux. Adding it during steelmaking and ironmaking can lower the melting point of slag, help remove impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus from ores, and improve metal purity; food-grade calcium carbonate can be used as an anti-caking agent and acidity regulator in food processing, such as preventing caking in flour, milk powder, and condiments, and adjusting acidity in beverages; in the pharmaceutical field, it can be used as a raw material for calcium supplements (such as calcium carbonate tablets) or as a filler in pharmaceutical preparations to adjust the dissolution rate of drugs; in the water treatment field, it can be used to neutralize acidic wastewater and remove heavy metal ions such as lead and cadmium from water through precipitation reactions to achieve water purification.