Calcium Carbonate Crusher Selection Guide: A Comprehensive Strategy from Requirements to Implementation
The selection of calcium carbonate crushers (mills) directly determines product quality, production efficiency, and overall costs. Especially since calcium carbonate serves as a core filler in industries such as building materials, plastics, coatings, and pharmaceuticals, the precise control of its fineness, purity, and particle size distribution is critical. Selection should follow the principle of “centering on production objectives, matching raw material characteristics, considering environmental protection and energy conservation, and strictly controlling cost risks”. The specific systematic steps are as follows:
I. First Clarify Core Production Objectives: Lock in the Basis for Selection
Before selection, it is necessary to accurately define three core indicators, which are the prerequisites for matching equipment types:
Finished Product Fineness Requirements
The fineness range of calcium carbonate products is extremely wide, from 60-mesh coarse powder for construction mortar to 2500-mesh nano-powder for medical use, corresponding to significant differences in equipment:
Coarse powder (80–400 mesh): Suitable for construction mortar, general coating fillers, etc., with low requirements for particle size uniformity.
Fine powder (400–1250 mesh): Used in plastic masterbatches, mid-range coatings, papermaking fillers, etc., requiring relatively narrow particle size distribution.
Ultra-fine powder (1250–2500 mesh, d97 ≤ 12μm): Applied in high-end coatings, pharmaceutical excipients, biodegradable plastics, etc., with extremely high requirements for classification accuracy.
Production Capacity Requirements
According to annual output, it can be divided into small and medium-scale (<50.000 tons), medium and large-scale (50.000–100.000 tons), and large-scale (>100.000 tons), which directly determine the single-machine capacity and production line configuration:
Small and medium-scale: A single-machine hourly output of 0.3–5 tons can meet the demand.
Large-scale: Large equipment with a single-machine hourly output of 4–50 tons is required, and continuous operation of the production line should be considered.
Finished Product Purity Standards
Pharmaceutical and food-grade calcium carbonate need strict control of metal impurities and dust pollution, requiring equipment with metal-free contact grinding; while calcium powder for building materials has lower purity requirements and can tolerate a small amount of impurities.
II. Mainstream Calcium Carbonate Crusher Types and Their Application Scenarios
At present, the mainstream equipment on the market includes three types: Raymond mills, ring roller mills, and ultra-fine vertical mills. In addition, jet mills are used for high-end ultra-fine powder production. The core application scenarios of various equipment are as follows:
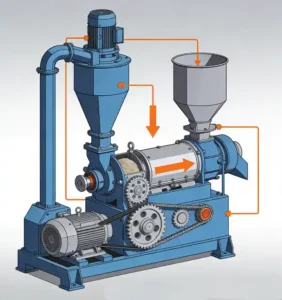
Raymond Mill: Cost-Effective Choice for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises
Core advantages: Low investment threshold (280.000–1.200.000 yuan), simple structure and easy operation, 99% pass rate for 80–400 mesh fineness, suitable for medium and low-hardness calcium-containing raw materials (Mohs hardness ≤ 7. such as calcite and limestone).
Technical highlights: The new generation of Raymond mills is equipped with an intelligent spring pressurization system, which can automatically lift the roller to avoid hard impurities, reducing equipment damage by 30%; the three-dimensional air separation system reduces dust overflow, with a measured emission ≤ 20mg/m³.
Application scenarios: Small and medium-sized enterprises with an annual output of <50.000 tons, producing 200–325 mesh calcium powder for construction, with an initial investment budget of <1.000.000 yuan. Typical case: A building materials factory in Liaoning uses a 4R3216 Raymond mill to produce 325 mesh hydrated lime powder, with a unit hourly output of 5.8 tons, a unit power consumption of only 28 kWh, saving 470.000 yuan in electricity costs annually.
Ring Roller Mill: “Dark Horse” in the Ultra-Fine Powder Field
Core advantages: Adopting multi-layer ring roller rolling technology, it can produce 400–2500 mesh ultra-fine powder in one step, with a specific surface area of 3.04m³/g and narrow particle size distribution; it covers only 1/3 of the area of traditional ball mill systems, does not require large-scale civil engineering, and shortens the commissioning cycle by 60%.
Application scenarios: Enterprises with an annual output of 50.000–100.000 tons that need to produce 400–2500 mesh fine/ultra-fine powder, especially suitable for raw materials with low humidity (≤ 6%). Typical case: A mining company in Guangdong uses an HCH-780 ring roller mill to produce heavy calcium powder with d97=12μm, successfully replacing orders from Taiwan-funded enterprises.
Ultra-Fine Vertical Mill: Cost-Reduction Tool for Large-Scale Production
Core advantages: Adopting bed material grinding technology, saving 30–50% energy; the intelligent temperature control system can keep the outlet temperature ≤ 95℃, protecting the activity of calcium powder; equipped with a turbo classifier, it can produce 3μm nano calcium powder, with a single-machine capacity of 4–50 tons/hour, suitable for large-scale continuous production.
Application scenarios: Large enterprises with an annual output of >100.000 tons, producing full-range calcium powder of 80–2500 mesh, especially suitable for high-hardness and high-humidity (≤ 15%) raw materials (can dry while grinding). Typical case: A company in Henan uses an HLMX1700 ultra-fine vertical mill to produce 1250 mesh calcium powder for biodegradable plastics, with a 100% D97 fineness qualification rate and an annual output exceeding 100.000 tons.
Jet Mill: Exclusive Equipment for High-End Ultra-Fine Powder
Core advantages: Adopting material self-collision grinding without metal contact, avoiding impurity pollution; the grinding temperature is close to room temperature (10–20℃), without thermal degradation risk, and can produce ultra-high purity ultra-fine powder with d97 ≤ 5μm.
Application scenarios: Production of pharmaceutical and food-grade calcium carbonate, or ultra-fine powder for papermaking coatings with d90 ≤ 2μm. The disadvantage is high investment and energy consumption.
III. Key Selection Factors: More Than “Can Produce”, but Also “Save Costs”
Raw Material Characteristic Adaptation
The hardness, humidity, particle size, and impurity content of raw materials directly affect equipment service life and operational stability:
Hardness: Raymond mills/ring roller mills are suitable for medium and low hardness (Mohs ≤ 7); vertical mills (equipped with high-chromium alloy rollers) are required for high hardness (Mohs 7–9.5).
Humidity: Raymond mills can be used for raw materials with moisture ≤ 6%; for moisture > 8%, vertical mills or ring roller mills with hot air systems should be selected (can dry while grinding) to avoid clogging.
Impurities: If raw materials contain hard foreign objects (such as metal blocks), vertical mills with automatic foreign object avoidance function should be selected; if they contain a lot of dust and impurities, magnetic separators and screening equipment should be equipped.
Environmental Protection and Policy Compliance
The new national standard in 2025 requires dust emission ≤ 15mg/m³, so attention should be paid to the environmental protection configuration of equipment during selection:
Raymond mills need additional pulse dust collectors to meet the standard.
Ring roller mills have a fully sealed design with emission ≤ 15mg/m³.
The intelligent dust removal system of ultra-fine vertical mills has emission ≤ 8mg/m³, fully meeting the requirements of green production.
Investment and Operation Costs
It is necessary to comprehensively consider initial investment, energy consumption, and maintenance costs:
Initial investment: Raymond mill (280.000–1.200.000 yuan) < ring roller mill (500.000–700.000 yuan) < ultra-fine vertical mill (2.000.000–8.000.000 yuan).
Energy consumption: Ultra-fine vertical mills are the most energy-saving (unit power consumption of 22–28 kWh for 600 mesh), followed by Raymond mills (28–38 kWh for 325 mesh), and ring roller mills have higher energy consumption for ultra-fine powder production (95 kWh when d97=10μm).
Maintenance cost: The wearing parts (rollers and rings) of Raymond mills need frequent replacement; vertical mills have long service life of wear-resistant materials and lower long-term maintenance costs.
IV. Comparison Table of Core Parameters of Mainstream Equipment
| Equipment Type | Applicable Fineness | Capacity Range | Unit Power Consumption (Typical Fineness) | Environmental Performance | Adaptable Raw Material Humidity |
| Raymond Mill | 80–400 mesh | 0.3–12t/h | 28–38 kWh (325 mesh) | Needs dust collector to meet emission standards | ≤ 6% |
| Ring Roller Mill | 400–2500 mesh | 0.8–5t/h | 95 kWh (d97=10μm) | Fully sealed, ≤ 15mg/m³ | ≤ 8% |
| Ultra-Fine Vertical Mill | 80–2500 mesh (secondary classification) | 4–50t/h | 22–28 kWh (600 mesh) | Intelligent dust removal, ≤ 8mg/m³ | ≤ 15% (with drying function) |
V. Selection Pitfall Guide: Three Common Mistakes and Solutions
Fineness Trap: Using General-Purpose Equipment to Produce Ultra-Fine Powder
Wrong case: A factory in Shandong uses a general-purpose Raymond mill to produce 800 mesh pharmaceutical calcium powder, with a qualification rate of only 65%. Solution: Ultra-fine powder (>800 mesh) must use ring roller mills, vertical mills or jet mills equipped with turbo classification systems to ensure classification accuracy.
Humidity Disaster: Ignoring Raw Material Moisture Leading to Clogging
Wrong case: Raw material moisture reaches 12% in rainy season, and Raymond mills of an enterprise in Guangxi frequently clog and stop production. Solution: When raw material moisture is >8%, select vertical mills or ring roller mills with hot air drying systems to realize grinding while drying; if Raymond mills are used, add a pre-drying process.
Over-Investment: Blindly Launching Large-Scale Equipment
Wrong case: A factory in Henan with an annual output of 30.000 tons chooses a large-scale vertical mill, resulting in no-load operation of the equipment and a surge in unit power consumption to 41 kWh. Solution: Choose Raymond mills for annual output <50.000 tons, ring roller mills for 50.000–100.000 tons, and ultra-fine vertical mills only for >100.000 tons. Matching capacity is the key to cost control.
VI. Summary: Selection Decision-Making Process
Clarify the three core objectives of finished product fineness, capacity, and purity; 2. Match equipment types according to objectives (Raymond mills for coarse powder, ring roller mills/jet mills for ultra-fine powder, vertical mills for large-scale production); 3. Verify equipment adaptability combined with raw material characteristics (hardness, humidity, impurities); 4. Compare investment and operation costs, considering environmental compliance; 5. Refer to industry cases to avoid selection pitfalls.