
How to cool the grinding zone in high-intensity milling
To cool the grinding zone in high-intensity milling, combineequipment-integrated cooling systems,direct heat extraction techniques,process optimization,...

How to design a complete calcium carbonate powder production line
A well-designed calcium carbonate powder production line requires careful planning of process flow, equipment selection,...

What is interparticle comminution and how does it work in roller mills?
Interparticle comminution (also called particle bed breakage or layer compression comminution) is a highly energy-efficient...
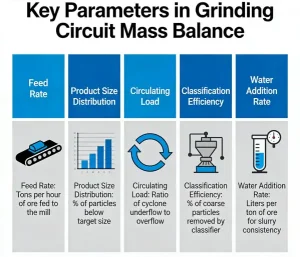
What are the key parameters in a grinding circuit mass balance?
A grinding circuit mass balance is a fundamental calculation in mineral processing used to quantify...

What is the purpose of a pre-drying system before grinding?
A pre-drying system before grinding serves several critical purposes, primarily focused on improving efficiency, product quality, and...

How to Produce Coated Calcium Carbonate (Stearic Acid, Titanate)
Coated calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) is produced via surface modification to convert hydrophilic CaCO₃ into hydrophobic/oleophilic...

How to grind calcium carbonate to 2 microns or less (nano grade)
To grind calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) to 2 microns or less (including nano-grade <100 nm), the...
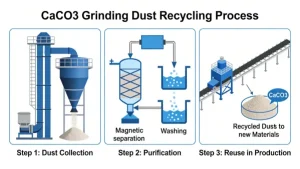
can CaCO3 grinding dust be recycled
Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) grinding dust is highly recyclable and widely reused in industrial processes, offering...

what is the pH of ultrafine CaCO3 slurry
The pH of ultrafine calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) slurry typically ranges from 8 to 10 under...

How to choose the right grinding mill for calcium carbonate
Start with a clear decision framework: first define production method (dry/wet), target fineness, and throughput,...

what safety measures for handling nano CaCO3 powder
While nano CaCO₃ is chemically inert and generally low-toxic, its nanoscale size creates unique inhalation...
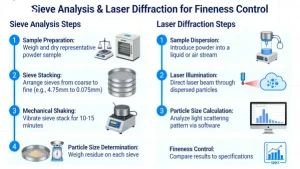
How to perform a sieve analysis and laser diffraction for fineness control
Fineness control is critical in mineral processing (e.g., calcium carbonate, graphite for lithium battery applications)...
